
According to their findings, 50.4% of available ECGs of patients showed changes relevant to critical hyperkalemia such as tall T waves, prolonged PR interval, shortening of QT interval, decreased P wave amplitude, sine-wave ventricular rhythms with big QRS complex, and ventricular fibrillation and asystole. They used commonly used medications for decreasing K + plasma levels, such as potassium-sparing diuretics, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, digoxin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and potassium supplements. suggested risk factors, clinical demonstration, and predictors of mortality of severe hyperkalemia. Otherwise, in severe hypokalemia, ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation, atrioventricular block, and tachyarrhythmias might be seen. In severe hypokalemia (potassium level under 3 mEq/l), the U-wave might outpace the T-wave therefore, the T-wave be masked by a giant U-wave, and the QU-interval might be considered a pseudo-prolonged QT-interval. Terminally in severe exceeding potassium levels, hemodialysis and sodium polystyrene sulfonate are represented as a prompt intervention. Due to transmembrane permeability changes in high potassium levels, there are some paths to suppress this condition such as intravenous calcium chloride infusion or a combination of glucose and insulin, which can transfer potassium from ECM to ICM, beta-2 adrenergic agonists, and also sodium bicarbonate. In this condition, as summarized by Figure 1, ECG changes, including expansive QRS complex, peaked T-wave, prolonged QT-interval, and hidden p-wave might be initiated. In this review, we summarize and evaluate the studies on electrocardiogram changes following potassium disorders.Īccording to many studies, hyperkalemia strongly correlates with ECG manifestations. Severe hyperkalemia and hypokalemia can threaten life, and immediate diagnosis and treatment are required.

In authoritarian states, cardiac arrest occurs in systole. In hypokalemia conditions (potassium levels become lower than 3.5 mmol/L), the cardiac cells hyperpolarise with a reduction in muscular contraction, heart rate, and blood pressure. In hyperkalemia conditions (potassium levels become higher than 5 mmol/L), the cardiac cells depolarise with almost no regular repolarization, which causes muscular weakness and in severe states, causes cardiac arrest in diastole. Therefore, increasing plasma potassium reduces this ratio, as a result, increases cell membrane excitability. Membrane resting potential is related to the difference between intracellular and extracellular potassium concentrations. Its increase or reduction has profound effects on the electrophysiology of cardiac muscle. The electrical stability of the heart is sensitive to potassium concentration. One essential electrolyte that impact transmembrane potential in cardiac cells is potassium concentration.

A significant ratio of cardiac arrests in adult patients with no coexisting cardiac disorder is due to metabolic abnormalities. Nowadays, ECG changes are one of the useful diagnostic clues for recognizing electrolyte abnormalities. Myocardial cells keep up their activity of depolarization and repolarization, by developing several essential electrolytes like potassium, sodium, and calcium their currents across the membrane can be announced by ECG.

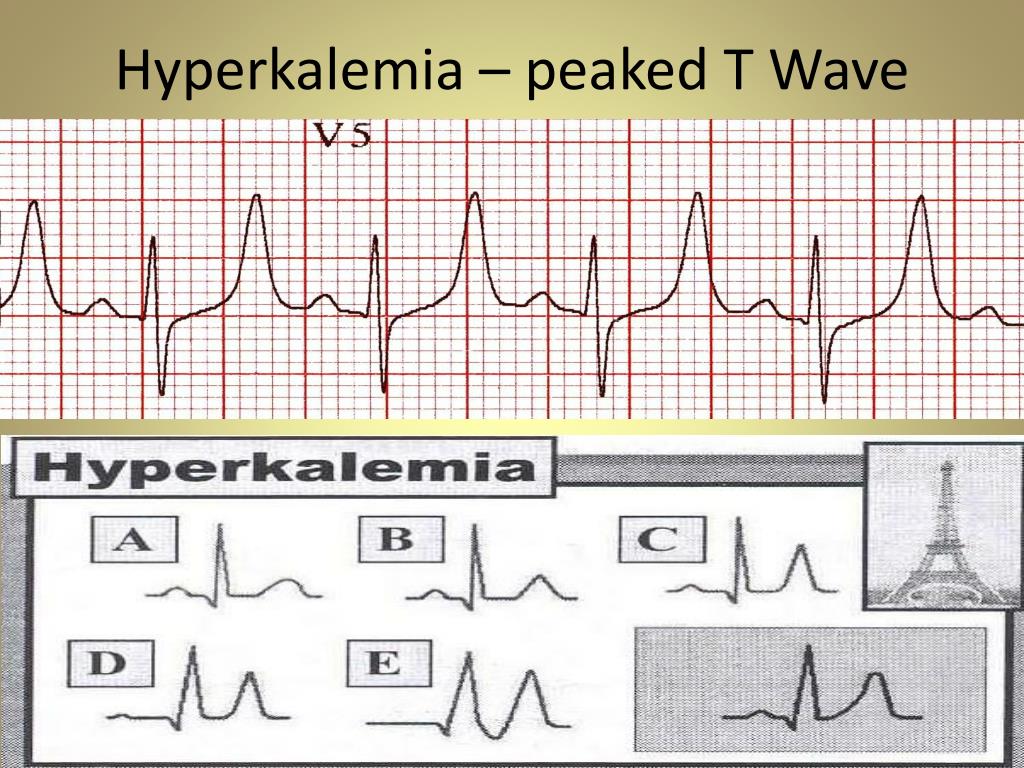
Manifestations change in hyperkalemia, for correct diagnosis clinical history of the patients is essential. ECG Changes in severe hyperkalemia that can endanger patients’ lives are noteworthy. The studies showed peaked T wave, as well as expanded QRS complex and low P amplitude, are important changes that can guide us to immediate diagnosis. Moreover animal studies on ECG changes related to hyper- and hypokalemia are provided. In this review, we summarized ECG changes related to hyperkalemia and interventions.
The current review summarizes studies to elucidate the correlation between potassium disorders and ECG demonstrations. Potassium disorders, including hyperkalemia and hypokalemia in authoritarian states, may lead to heart dysfunctions and could be life-threatening, and urgent interventions are needed in this conditions. Potassium is one of the essential electrolytes in cardiac cells, and its variations affect ECG. Nowadays, electrocardiogram (ECG) changes are one of the valuable diagnostic clues for recognizing abnormalities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
